
Since the early 2000s, the automotive sector in Brazil has been constantly expanding and developing, reaching double-digit growth of more than 20% in both production and sales in 2017 compared to 2016, making the industry in Brazil one of the largest in the region and the world.
According to the latest annual data for 2019, the country has become the second-largest producer of motor vehicles in Latin America after Mexico with more than 2.9mn vehicles produced, up by almost 2% y/y. Brazil is also the sixth-largest automobile market in the world with almost 2.8mn newly registered cars in 2019, following China with 21mn, the US with almost 17mn, the EU with 15mn, Japan with 4.3mn and India with almost 3mn new car registrations. Vehicle sales, both domestic and international, reached 2.9mn units in 2019. The industry has been of increasing importance over the years and in 2018 it netted revenues of almost USD 62bn. According to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics, the automotive sector had a 0.35% share of GDP in 2017.
The quick growth of the industry has been mainly due to the foreign investments made by some of the largest automobile producers in the world. Popular car makers such as BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Audi, Volkswagen, Fiat, Citroen, Mitsubishi, Kia, Land Rover, Suzuki, Nissan, and Honda have been building factories in Brazil, creating many new job opportunities, lowering the unemployment rate and boosting the national economy. Another key factor for the growth of the industry in Brazil has been the increasing consumer and business confidence, combined with the relatively low borrowing costs - the Selic rate has been steadily decreasing form 14% in 2016 to 2% in August 2020. This favourable environment has increased the overall domestic demand. The automobile industry has been accounting for around 15% of Brazil’s industrial GDP since the start of the rapid growth of the industry two decades ago. According to 2017 data, the gross value added of the automobile production, which includes cars, trucks and busses was around USD 6.2bn.
The government has also been a key player in the efforts towards improving the business environment and creating incentives for the technological development, competitiveness and increasing foreign investment in the automobile industry in Brazil. The Rota 2030 (Route 2030) programme, launched in December 2018, has been a great aid to the development and growth of the industry and also to the attempts in promoting Brazil as a worldwide champion in the car manufacturing and trade business. Rota 2030 presents many opportunities for investors by setting a 3% tax break on the industrial components used in hybrid and electrical vehicles sourced locally, which provides support not only for producers but for local suppliers as well. The programme also includes a USD 400mn (around BRL 2.2bn) annual tax credit for industry manufacturers who are willing to invest around USD 900mn (BRL 5bn) into research and development annually.
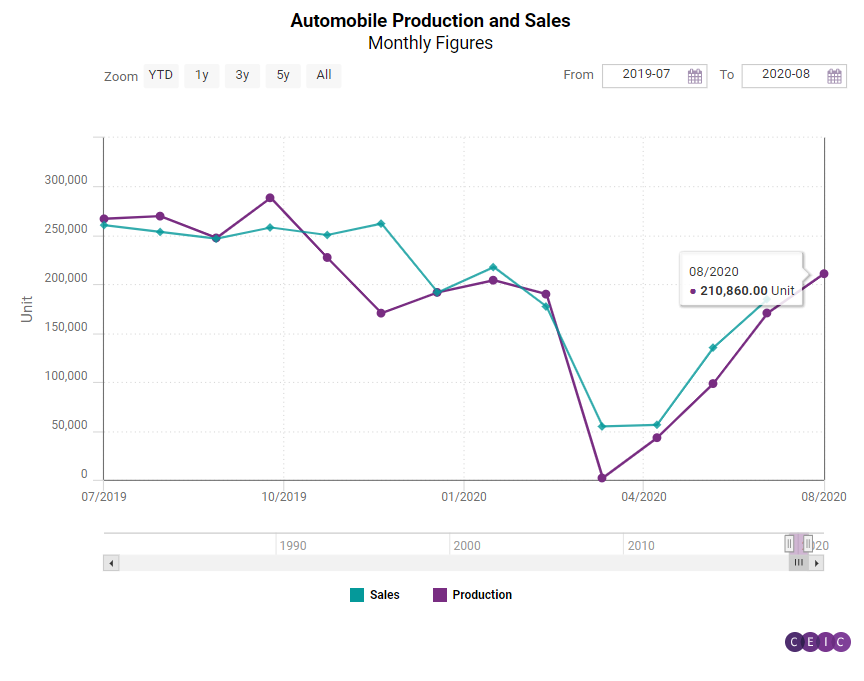
The Brazilian government has also made an effort to promote vehicle exports and facilitate new trade agreements with other Latin American countries. Brazil is a member state of the Southern Common Market (Mercosur), whose members can trade between themselves at preferential tariffs under the Latin American Integration Association (LAIA/ALADI) framework through an Economic Complementation Agreement (ACE-18). The LAIA/ALADI has the ultimate goal of gradually establishing a single market in Latin America which has the potential to make the bloc an even larger global trade power. The year 2020 has not been a good one for the automotive industry in Brazil so far, as the ongoing COVID-19 crisis has been affecting manufacturing industries around the globe. In April 2020, Brazil reported an all-time record drop in automobile production to a mere 1,800 units. In May and June some recovery was observed, however, the growing number of confirmed COVID-19 cases in August may undermine this fragile recovery.
Automobile Production
At its peak in 2013, the output of Brazil’s motor vehicle industry reached a record 3.7mn units. This record was followed by a downward trend, with output going down to 3.1mn units in 2015, 2.4mn in 2016 and a 12-year low of 2.1mn units in 2016. There has been a gradual recovery since then and in 2017 the industry registered a 25.4% growth y/y and continued improving ever since. The latest figures for 2019 show a production output of 2.9mn vehicles but the COVID-19 outbreak has already had a big effect the output of the industry in 2020 and will most likely have a lasting impact in the following years.
Passenger cars made up the bulk of the sector output in 2019 with 2.4mn units, followed by light commercial vehicles with a little over 350,000 units, trucks with 113,000 units and buses with almost 28,000 units. Manufacturers such as Ford and General Motors (GM) set foot on the Brazilian market as early as in the 1920s and 1940s, followed by many others such as Volkswagen, Fiat, Mercedes-Benz, Hyundai, Toyota, Peugeot, and Nissan. The largest producer of cars in Brazil since 2016 has been GM with its flagship brand Chevrolet, accounting for an average of around 400,000 cars produced every year since then. GM is followed by Volkswagen and Fiat with 350,000 and 316,000 cars, respectively. The latter two companies have gradually decreased their output since 2010, when Volkswagen produced almost 1mn cars and Fiat’s output was almost 600,000 cars. GM has seven facilities in Brazil, including manufacturing and assembly sites, customer care & aftersales facilities, as well as research, development, and corporate offices. In contrast, Fiat has only one factory in Betim in the state of Minas Gerais and Volkswagen has four factories of which three are in the Sao Paulo state and one is in Paraná.
Over the years, along with vehicles, the production lines started to manufacture auto parts - at first only for the sake of the manufacturers' needs. Later on, following the increasing demand, retail sellers started providing customers with replacement components and additional care for the vehicles, which incentivised the birth of the independent motor vehicle parts replacement market and created a whole new segmentation of the auto part industry in Brazil. As of 2018, the revenue from auto part replacement sales accounted for almost 20% of the total revenue coming from the entire auto parts industry, preceded only by the auto part revenue coming from the automobile industry manufacturers with 63%.
As the competition among automobile manufacturers increases, the extent to which a company can use its installed capacity becomes increasingly important. However, production lines are, as a rule, customised to produce a given model in order to achieve a higher volume yield and this limits the number of features that producers can offer. But demand is always changing and consumers are constantly seeking new features and improvements. That said, when the demand for a specific model fades in favour of newer models, the adjustment of production lines becomes necessary but also very tough and this leads to periodical decreases in capacity utilisation. As a country which feeds mainly the local demand, Brazil-based manufacturers often face this issue and the capacity utilisation in the factories has been varying between 50% and 70%. April 2020 is a notable exception, as the rate fell to as low as 32% due to the social distancing measures imposed in a bid to control the COVID-19 outbreak.
Labour Market and Labour Cost
As the automotive industry in Brazil has been steadily developing and expanding, the labour market has also been adjusting to accommodate the increasing demand for workers in the industry. According to the Brazilian Automotive Industry Association, as of December 2019, 1.3mn of people worked in the automotive segment, considering direct and indirect jobs. About 400,000 people worked for the 26 car manufacturers nand the 473 producers of autoparts in the country, while more than 900,000 people worked with the commerce and repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles.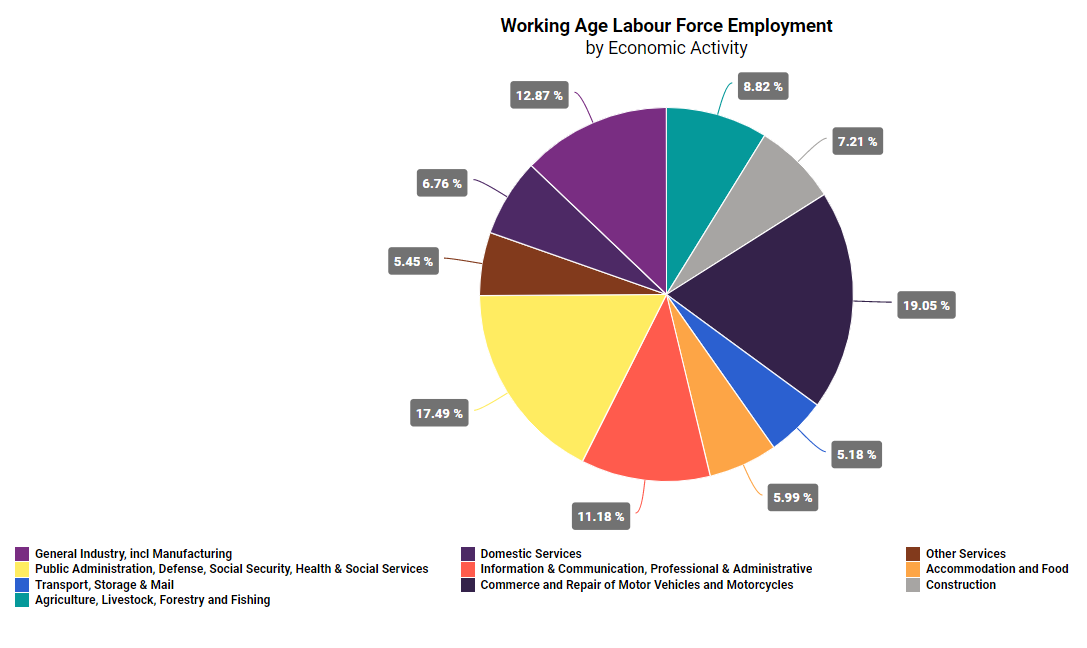
According to the Salary Explorer, in 2020 the wage of an automotive technician in Brazil varies from BRL 1,660 (around USD 319) to BRL 5,270 (around USD 1,013) per month, depending mainly on the years of experience and seniority of the worker. This is close to the private sector average monthly wage in Brazil, which is currently around USD 500 per month.
Sign in to read the full data analysis on Brazil's automotive sector here. Alternatively, download the latest, comprehensive analysis of Brazil's economy with the CEIC Brazil Economy in a Snapshot Q2 2020 Report.
.png?width=160&name=ceic-logo-Vector%20logo%20no%20tagline%20(002).png)
